Toward human-centered healthcare: Understanding, measuring, and promoting Co-Creation of Care (CCC) as a mutually beneficial interaction between healthcare staff and patients
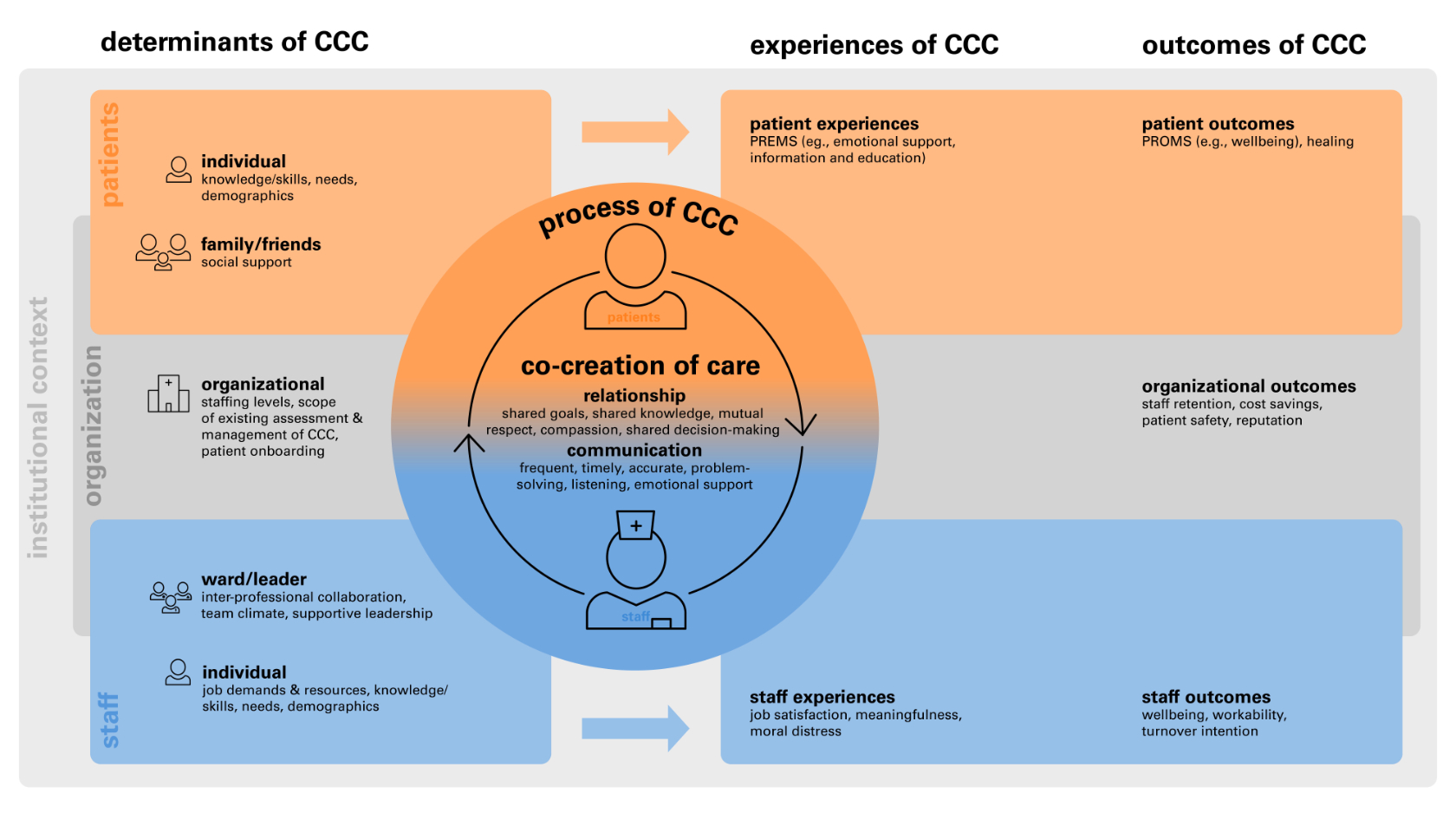
The healthcare system is facing major challenges: an aging population, increasing chronic diseases, and rising costs are putting pressure on the system. At the same time, there is a shortage of skilled personnel, especially nursing staff, which is further exacerbating working conditions in many places. In this tense environment, both patients and professionals are coming under increasing pressure. People-centered care is considered key to sustainable improvement. The “Co-Creation of Care” (CCC) project focuses on direct interaction between nursing staff and patients: the “co-creation of care.” What does CCC mean? It means the joint design of care by nursing professionals and patients in everyday hospital life. It is about interaction, communication, and relationship building—not in theory, but in the concrete care process on the ward. Both sides are seen as active contributors and beneficiaries.
Involved Researchers
Short Description
The interdisciplinary research project “Co-Creation of Care” investigates how everyday cooperation between nursing staff and patients can be made more humane, more collaborative, and at the same time more effective. The focus is on how such Co-Creation of Care (CCC) is actually practiced in everyday hospital life and how it affects the satisfaction and well-being of both sides. Together with several Swiss hospitals, we are conducting qualitative and quantitative surveys (including interviews, observations, questionnaires, and cultural probes) to identify key elements of successful interaction. The aim is to develop practical recommendations for the systematic promotion of CCC and thus contribute to improving working conditions, patient experience, and quality of care. The project is supported by five research teams based at the University of Zurich (UZH), the Zurich University of Applied Sciences (ZHAW), the Zurich University of the Arts (ZHdK), and the University Hospital Zurich (USZ).
Project Partners
- UZH:
- Institut für Epidemiologie, Biostatistik und Prävention (EBPI) Public & Organizational Health und Center of Salutogenese
- Institute of Biomedical Ethics and Medical History, (IBME),
- ZHdK Institute of Design Research (IDR)
- ZHAW School of Management and Law Management im Gesundheitswesen
- various partners from hospitals including University Hospital Zurich.
Financed by: Swiss National Science Foundation (SNF); Grant Nr. 10003791
Duration: June 2025 – November 2028